Introduction
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is an important food legume and is a main source of protein, hence its nickname ‘poor man’s meat’ (Broughton et al. 2003). It plays a vital role in agriculture by associating with rhizobia and fixing atmospheric N2 through a biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) process. A wide range of rhizobia is known to associate with beans due to its promiscuous nature and these different strains are likely to vary in their BNF potential. Thus, with the aim of identifying more effective rhizobia, we trapped new strains from bean growing areas in Southern Ethiopia and genotyped them to determine their taxonomic identity and relatedness to reference strains of known N2 fixing ability.
|
Materials and Methods
Phaseolus vulgaris nodulating rhizobial strains were trapped from soil using Nasir, Ebado and Hawassa dume bean varieties. The strains were amplified using colony PCR for symbiotic (nodC and nifH), housekeeping (glnII, gyrB, recA and rpoB) and 16S ribosomal RNA genes. Cleaned PCR products were sequenced by Macrogen Inc. The Netherlands. The quality of the DNA sequences were checked by BioEdit package and blasted to sequences in Gene bank using nucleotide blast method in NCBI. The sequences were then aligned by ClustalW in MEGA7 (Thompson et al. 1994) and a Neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed based on a pairwise distance matrix using Tamura’s 3-parameter substitution model with complete deletion of gaps. Robustness of the tree topology was evaluated using 1000 boot strap iterations (Kumar et al. 2016). Here, we present a phylogeny of concatenated loci (glnII, gyrB and recA).
Results and Discussion
The evolutionary phylogeny based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) grouped the new strains into VI clusters and mostly with Rhizobium etli (CFN42), R. phaseoli (ATCC14482), R. aethiopicum (HBR26) and R. etli bv. phaseoli (IE4803) type strains, cluster I-V (Fig. 1). Strains (NAK91 and NAK103) originated from Kenya and one of our new isolate NAE165 clustered (cluster VI) with R. tropici (CIAT899) commercial strain at 100% boot strap of nucleotide similarity. In a previous study using 16S rRNA and concatenated recA and atpD genes, NAK103 was grouped with R. phaseoli (ATCC14482) (Mwenda et al. 2018). This difference might be due to mislabelling during sharing the strains or due to differences in resolution capacity of the loci used. A few new isolates such NAE6, NAE55, etc. clustered with Agrobacterium radiobacter (LMG140).
Conclusions
Our new Ethiopian isolates are mostly related to R. etli and R. phaseoli groups. Strains in cluster II may be a new genospecies and need to be further investigated.
|
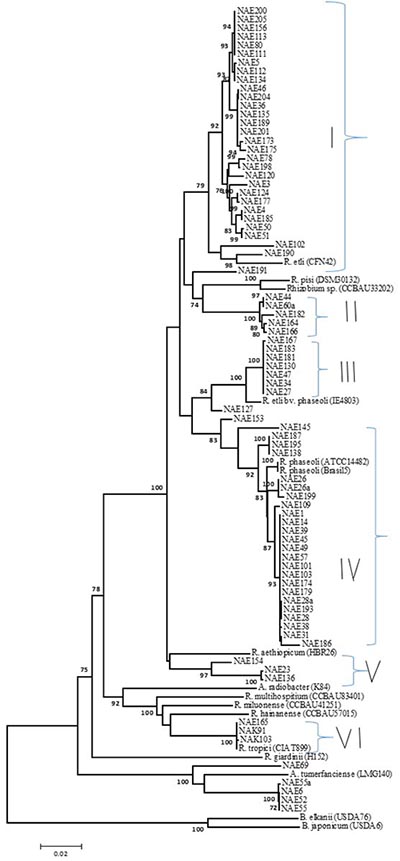
Figure 1: Neighbour-joining phylogeny of MLSA
|
Ashenafi Hailu Gunnabo, Wageningen University & Research, The Netherlands (Click here for his 2017 update)
References
- 10.1016/j.syapm.2011.11.005
- Broughton WJ, Hernandez G, Blair M, et al (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.) - model food legumes W. Plant Soil 252:55–128. doi: 10.1023/A:1024146710611
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Evol Genet Anal 33:1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
- Mwenda GM, O’Hara GW, De Meyer SE, et al (2018) Genetic diversity and symbiotic effectiveness of Phaseolus vulgaris -nodulating rhizobia in Kenya. Syst Appl Microbiol. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2018.02.001
- Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673

