| Introduction |
|
N2Africa is a large scale, science-based “research-in-development” project funded by The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and focused on putting nitrogen fixation to work for smallholder farmers growing legume crops in Africa. N2Africa aims to enhance productivity of grain legumes of smallholder farmers which in turn helps to increase income, improve household nutrition, and enhance soil fertility. The vision of success is to build sustainable, long-term partnerships to enable African smallholder farmers to benefit from symbiotic N2-fixation by grain legumes through effective production technologies, including improved seeds, inoculants and fertilizers, linking scientific knowledge with capacity building. ...
Photo: Field visit DR Congo (Credit: J.M. Sanginga)
|
 |
|
1 |
| N2Africa DRC exit and continuation by partners |
 |
N2Africa works in two out of the twenty-six provinces in DRC: North and South Kivu. In total the project covers twenty-six action sites across various agro-ecological zones: mountains and valleys with large differences in soil types ...
Photo: IKYA/UPSKI visit the soya processing facilities at the Centre Olame, Bukavu DRC
|
|
2 |
| Partner PAD and N2Africa |
| PAD (Programme d’Appui au Developpement Durable) is a Congolese NGO that was established in 2001. It is based in Bukavu in the eastern part of the Democratic republic of Congo (DRC). PAD has a professional staff specialized in rural areas, dissemination of innovative agricultural technologies, and cooperative movement. Globally, PAD aims for sustainable improvement of the socio-economic status of rural populations in eastern DRC. ... |
 |
|
3 |
| Kenya’s N2Africa actions in 2017 and exit strategy |
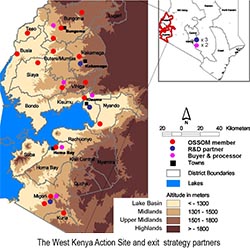 |
The final year of N2Africa in Kenya was committed to positioning for lasting project impact. Kenya’s N2Africa exit strategy is based on several intersecting goals. Input manufacturers and seed companies will continue to invest in legume production inputs, and expand their scope of operations, including greater incentives to “last mile” agrodealers. MIRCEN will continue to provide independent testing of biofertilizers and legume inoculants. ... |
|
4 |
| MIRCEN will continue its rhizobiology services |
The Microbial Resource Center (MIRCEN) was established at the University of Nairobi long before the N2Africa Project (1977) and will continue its work afterward. Our activities include testing legume inoculants and other bio-fertilizers, maintaining a small working culture collection of symbiotic micro-organisms and conducting training and research on soil microbiology. The past eight years that MIRCEN has worked closely with N2Africa have proven mutually beneficial. ...
|
5 |
| OSSOM’s awesome future |
|
The One Stop Shop Operations Mechanism (OSSOM) was started in Kenya at the beginning of 2017 to better link “last mile” agrodealers to commercial manufacturers and distributors of BNF technologies. This move followed three year’s reliance upon the Western Region Agricultural Technology Evaluation (WeRATE) as N2Africa’s main outreach partner in west Kenya, an umbrella organization comprising 28 farmer associations. ...
Photo: BNF technology demonstration at an OSSOM Customer Open House
|
 |
|
6 |
| N2Africa-Malawi: moving forward beyond 2017 |
 |
N2Africa in Malawi started its work in 2010 and has been operating in seven administrative districts of Lilongwe, Dedza, Ntcheu, Salima, Dowa, Kasungu, Mchinji. It worked with partners ...
Photo: Demonstration plot-single row vs double row planting of groundnuts
|
|
7 |
| Strides in inoculant production and distribution in Malawi - the story of AISL |
|
Prior to 2015, awareness of the advantages of soyabean inoculation was created among farmers in Malawi by N2Africa, but soyabean inoculant remained largely unavailable to farmers. Inoculant production was mostly limited to research (with only a few hundred sachets being sold to farmers) through the government’s Department of Agriculture Research Services (DARS). This public institution was unable to scale its production to meet the inoculant demand. This was the situation until 2015, when Agro-Input Suppliers Limited (AISL) stepped in ...
Photo: AISL Laboratory under construction in Kanengo Lilongwe. The expected completion date is January 2018 and ready for use in March 2018.
|
 |
|
8 |
| N2Africa experiences: Mozambique |
 |
owards the end the N2Africa project focused on scaling out the legume technologies proven under Phase I using a “business-led” approach. This involved engaging government, development organizations, and the private sector, creating awareness on N2Africa technologies and approaches, and facilitating dissemination campaigns. ...
Photo: Maria Miguel Noe now provides seeds to her community. Photo credits Wilson Leonardo
|
|
9 |
| ACOF and N2Africa: the soyabean partnership |
|
Agro Commercial Olinda Fondo (ACOF) is a woman-headed agribusiness company based in Mocuba District of Zambezia Province in Mozambique. ACOF produces and markets soyabeans and maize, selling mostly to the poultry industry. To supplement its own production, ACOF has an outgrower scheme involving women smallholder farmer groups in several districts ...
Photo: Wilson Leonardo showing a farmer how to thin a soyabean field for optimal density (Photo credits Wilson Leonardo)
|
 |
|
10 |
| Strategic scenario to close the gaps identified in Rwanda |
 |
N2Africa activities were initially introduced in three provinces, namely Eastern, Northern, and Southern Provinces of Rwanda. In Phase 2, activities were scaled up in Western Province by partners operating there.
BNF technologies promoted by N2Africa in Rwanda were centered around two legume species: common bean (bush and climbing), and soyabean.
Picture: Carte administrative de Rwanda
|
|
11 |
| DRD partnering into the future |
Current approach
N2Africa’s partnership with DRD (Developpement Rural Durable) has been focused on the production of climbing beans. It has been a fruitful collaboration. Before the partnership, many farmers used only local bean varieties with low production, and with limited skills in agronomic practices, whereas now farmers have adopted improved practices. ... |
 |
|
12 |
| COCOF and the soyabean value chain |
 |
The original French article is accessible via the English summary.
COCOF is a Rwandese organization created in 1994 by a group of rural women from the district of Kamonyi, with the aim to promote the socio, economic and political development of women. To date COCOF has 482 women members and 5881 beneficiaries with 68% women and 32% men. Beneficiaries are grouped in cooperatives.
Photo: Assamblée générale de COCOF
|
|
13 |
| Zimbabwe N2Africa project exit strategy |
|
After eight good years of working with thousands of smallholder farmers across seven districts during Phase I and five districts during Phase II, N2Africa Zimbabwe is now wrapping up the active funding phase of the project. In Zimbabwe, we are entering ‘Phase III’ ...
Photo: Farmers used grain they had produced to make more valuable products
|
 |
|
14 |
| N2Africa reinforced nutrition education for HIV-AIDS care groups in Zimbabwe |
 |
The Cluster Agriculture Development Services (CADS) implemented the N2Africa project activities during the last six years, principally in Goromonzi and Mutoko districts. CADS fosters better livelihoods for various communities faced with different challenges. ...
Photo: Farmers at a groundnut field day in Mutoko district
|
|
15 |















